R. ferrumequinum is the largest European horseshoe bat with a wingspan of 330-400 mm and its soft fur changes from grey as a juvenile to grey-brown in adulthood. As with other Rhinolophidae, it has a complex nose structure which resembles a horseshoe and contributes towards its highly specialised echolocation system.
Decreasing according to the IUCN Red List.
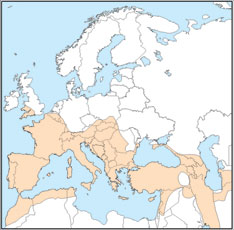
This species occurs from North Africa and southern Europe through south-west Asia, the Caucasus, Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan and the Himalayas to south-eastern China, Korea, and Japan.
R. ferrumequinum has shown marked decline in northwest Europe, and become almost extinct in Germany. Reasons for the decline are the use of highly toxic pesticides in agriculture and forestry and timber preservative in roosts. Other threats include habitat loss and fragmentation, reduction of food availability, and roost disturbance.

