The Lesser Horseshoe bat is the smallest European horseshoe bat with a wingspan of 190-254 mm. It has soft, fluffy brown fur, small strong feet and very broad, rounded wings, with which it wraps itself during hibernation. It can be distinguished from other Rhinolophidae not only because of its size but also because of its longer and pointier sella tip.
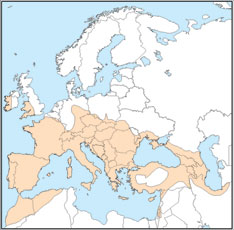
Distributed across most of Europe, it can be found in warmer regions with woodlands, riparian forests and pastures. The selection of roosts depends on the temperature; large rock crevices and attics of buildings are chosen for summer, while caves, tunnels and mines are used during winter. Maternity colonies can reach 500 individuals but these hang individually and not in clusters.
R. hipposideros are very agile, which allows them to quickly narrow the distance between them and their prey. While in flight, they are able to glean crane-flies, lacewings, moths and spiders from branches. Similarly to other Rhinolophidae, the Lesser Horseshoe bat is rather sedentary and the average distance between its roosts ranges from 5-50 km. Longer migrations have also been recorded.